About the hardware circuit knowledge of mobile phone Camera
August 3, 2023
1. Hardware circuit
![]()
hardware power
Camera is generally inseparable from these four circuits.
AVDD
DVDD
IOVDD
AFVDD
in
1. AVDD
Sensor analog power supply. It mainly supplies power to the internal photosensitive area and ADC, which is a sensitive power supply. Water ripples in the camera preview or large noise in dark conditions are generally caused by dirty AVDD power supply. Multiple cameras working at different times can share one AVDD. The AVDD of the front and rear main cameras cannot be shared. Although some cameras can be shared, they must also be designed for LDO reservation, and the reserved LDO is given priority as the backup of large pixels. The AVDD input of each Camera must reserve an RC filter network for debugging needs.
2. IOVDD
IO interface power supply. It mainly supplies power to internal I2C and MIPI. At the same time, the power of the IO usually shares a set of power with the I2C pull-up source corresponding to the Camera. The power consumption is the lowest, belonging to the uA level. Insensitive to noise, low impact.
3. AFVDD
Focus motor power. In the main camera of the mobile phone, there is often a circuit called AFVDD. The main function is to achieve focus. The voice coil motor (VCM) of the mobile phone camera needs the cooperation of the Driver IC to complete the focusing. Both of its two PINs are connected to the Driver IC. In a permanent magnetic field, the DC size of the inner coil of the motor is changed by the Driver IC to control the stretching position of the spring leaf, thereby driving up and down movement.
Try to turn on or off the rear camera, and you can hear the impact sound caused by the movement of the voice coil motor. At the same time, when the camera is turned off, the closer the mobile phone is to the subject, the more obvious the sound will be when it is turned off, and the farther it is from the subject, the less audible the sound will be.
There is a knocking sound when it is turned on
Turn on or restart the camera for the first time, the initial position of the motor drive is the bottom end of the effective stroke of the motor. If the
stroke is large, it is easy to hit the base. If you want to optimize this kind of problem, you can choose to modify the initialization position and change it to the middle of the stroke.
hardware signal
1. I2C
The communication method between Camera and BB chip belongs to I2C. The rate is generally 400K. Cameras that can work at the same time, such as the front and rear main cameras, cannot share a set of I2C, so as to avoid insufficient I2C bandwidth, reduce the response speed of the Camera to the Host, and increase the response delay of the Camera.
2. MCLK
In addition to several important power supplies, there is also a clock signal, which is provided by the BB chip with a frequency of 24M. It is the clock source of the CCM sensor. MCLK is processed by the sensor and becomes the PCLK required for data transmission. PCLK refers to the clock for pixel sampling. A magnetic bead is often strung on its path to solve the problem of radio frequency desense.
3. VSYNC
Field synchronization signal. Multiple cameras under dual-camera need to expose data at the same time. Therefore, the VSYNC of each Camera is connected together for synchronization. Cameres working at the same time should be separated by 0R resistors for debugging.
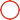
PCB design
![]()
Place the capacitors according to the diagram, and place them close to the corresponding pins (the PMU output capacitor is close to the PMU, and the Camera decoupling capacitor is close to the connector).
AVDD: RC filter combination is placed close to the connector; 0.1uF is placed close to the connector, followed by 4.7uF. The ground of the capacitor is connected with the analog ground AGND on the Camera module and connected to the main ground through Via near the connector. If the LDO is reserved, it is also required to be placed close to the connector. AVDD is well protected, and the wiring is three-dimensionally covered. Make as few holes as possible and change layers, and it is forbidden to run parallel or adjacent to current, RF and clock signals.
DVDD: The capacitor is placed close to the connector. Due to the large current, the line width is required to meet the corresponding current value.
IOVDD: The capacitor is placed close to the connector, the current is small, and the basic line width is sufficient.
AFVDD: Same as AVDD. The pin of AFGND is directly connected to the negative pole of the corresponding decoupling capacitor and is close to the main ground under the socket. There should be no physical connection to the GND net of other layers.
The line widths of the three circuits are all designed in the way of 1A 1mm line width.
MIPI: Common mode inductors are usually connected in series, but current projects often choose to omit them. Test points for MIPI signal testing need to be placed on the MIPI path. Keep inner layer routing, except BB and connector end, avoid surface layer routing. No more than 4 holes are punched for the entire path. After the layer is changed, the wiring still maintains a complete reference ground plane, and each group of MIPI Data and MIPI CLK is separately packaged for processing. If it is not possible to deal with separate land parcels, groups must maintain the 3W principle. The differential impedance is controlled at 100ohm±10%. The equal length of P and N in the differential is controlled at 15mil, and the intergroup is controlled at 40mil.
MCLK: belongs to the high-speed signal. Make a three-dimensional package. Use a pogo pin test during measurement to ensure that the tested waveform will not be distorted. If the MCLK signal is not well protected and the waveform is abnormal, it will also show that there are serious defects in the effect.
The surface layer and sub-surface layer under the connector should keep the GND intact and cannot be routed.