[Camera] Camera module hardware
February 28, 2023
1.Introduction
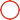
Camera module, full name CameraCompact Module, CCM for short. CCM consists of four major parts: lens (lens), sensor (sensor), flexible board (FPC), and image processing chip (DSP). The important components that determine the quality of a camera are: lens (lens), image processing chip (DSP), sensor (sensor). The key technologies of CCM include: optical design technology, aspheric mirror manufacturing technology, and optical coating technology.
Working principle: The light collected by the object through the lens (lens), converts the optical signal into an electrical signal through a CMOS or CCD integrated circuit, and then converts it into a digital image signal through the internal image processor (ISP) and outputs it to the digital signal processor (DSP) process and convert image signals into standard GRB, YUV and other formats.
2. Hardware composition
2.1 Lens (lens)
Lens is a device that can receive light signals and converge the light signals to the photosensitive device CMOS/CCD. Lens determines the lighting rate of the sensor, and its overall effect is relative to a convex lens.
Generally, the lens structure of a camera is composed of several lenses, including plastic lenses (PLASTIC) and glass lenses (GLASS). Usually, the lens structures used by CAMERA include: 1P, 2P, 1G1P, 1G3P, 2G2P, 4G, 8P, etc. The more lenses, the higher the cost; glass lenses are more expensive than plastic lenses, but the imaging effect of glass lenses is better than that of plastic lenses. At present, the cameras configured for mobile phones in the market are mainly 1G3P (composed of 1 glass lens and 3 plastic lenses) in order to reduce costs.
2.1.1 Main Indicators of Lens
A. Eliminate as many Flares as possible
B. Image clarity
C. CRA (Chief Ray Angle) must match and reduce shading (Lens cra < Sensor CRA, the difference should be within 2 degrees)
D, the aperture as large as possible
E, Distortion as slight as possible, etc.
2.1.2 Main parameters of Lens
(1) Focal length: The focal length of the lens determines the size of the captured image, the size of the field of view, the size of the depth of field and the perspective of the picture. Generally speaking, for a single-lens lens, it is the distance from the center of the lens to the focal point, while a camera lens is composed of multiple lenses, which is much more complicated. The focal length here refers to the distance from the center point of the lens to the clear image formed on the photosensitive device (CCD).
(2) Field of view: We often use the horizontal field of view to reflect the shooting range of the picture. The larger the focal length f, the smaller the angle of view, and the smaller the range of images formed on the photosensitive element; on the contrary, the smaller the focal length f, the larger the angle of view, and the larger the range of images formed on the photosensitive element.
(3) F value (aperture ratio): F value refers to the brightness of the lens (that is, the amount of light transmitted by the lens). F=lens focal length/aperture diameter. For the same F value, the aperture of a long focal length lens is larger than that of a short focal length lens.
(4) Aperture: The aperture is an adjustable optical-mechanical aperture located inside the lens, which can be used to control the amount of light passing through the lens. Variable aperture (Iris diaphragm). The mechanical device inside the lens to control the size of the aperture. Or refers to the device used to open or close the aperture of the lens to adjust the f-stop of the lens.
(5) Depth of field: When an object is in focus, all objects within a certain distance from the front of the object to a certain distance behind it are equivalent to being clear. The distance from front to back where the focus is fairly sharp is called depth of field.
2.2 VCM (Voice Coil Motor) voice coil motor
The full name is Voice Coil Montor, a voice coil motor in electronics, which is a kind of motor. Because the principle is similar to that of a speaker, it is called a voice coil motor, which has the characteristics of high frequency response and high precision. Its main principle is to control the stretching position of the spring leaf by changing the DC current of the inner coil of the motor in a permanent magnetic field, thereby driving the up and down movement. Mobile phone cameras widely use VCM to realize the auto-focus function, through which the position of the lens can be adjusted to present a clear image.
2.2.1 VCM performance index
The performance of VCM mainly depends on the ratio of current to travel distance. Starting from the starting current, the current rise should be proportional to the travel distance that can be driven. The smaller the required rising current, the higher the accuracy. At the same time, it also depends on the maximum power consumption, maximum power, and size.
2.2.2 Classification of VCMs
From the structure can be roughly divided into three categories: (1) shrapnel structure; (2) ball structure; (3) friction structure.
In terms of function, it can be roughly divided into five categories: (1) Open loop open motor; (2) Close loop closed-loop motor; (3) Alternate mid-mounted motor; (4) OIS optical image stabilization motor (divided into translation type, shifting shaft type, Memory metal type, etc.); (5) OIS+Close loop six-axis motor.
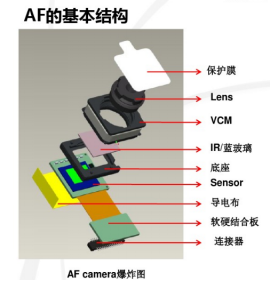
2.2.3 Principle of AF
After entering the auto-focus mode, the Driver moves from 0 to the maximum value, so that the lens moves from the original position to the maximum displacement position. At this time, the sensor imaging surface automatically takes pictures and saves them in the DSP. The DSP calculates each picture through these pictures. MTF (Modulation transfer function) value, so as to find the maximum value in this MTF curve, and through the algorithm, get the current corresponding to this point, and once again instruct the Driver to provide this current to the voice coil, so that the lens stabilizes at this imaging face, so that automatic zooming is achieved.
2.2.4 Zoom and focus
A: Realize optical zoom using zoom motor (ZOOM)
By moving the lens inside the lens to change the position of the focal point, the length of the focal length of the lens, and the size of the viewing angle of the lens, so as to achieve the magnification and reduction of the impact.
B: Realize autofocus using focus motor (AF)
Move the position of the entire lens (rather than the lens inside the lens) over a small distance to control the focal length of the lens to achieve clear images. This method is commonly used in mobile phones.
Optical focus and optical zoom are different concepts:
Optical zoom is to change the position of the focal point by moving the relative position of the lens inside the lens, change the length of the focal length of the lens, and change the viewing angle of the lens, so as to realize the enlargement and reduction of the image;
Optical focusing is actually to adjust the position of the entire lens (not the lens inside the lens) to control the image distance, so as to make the image clearest.
2.3 IR-CUT
There are various wavelengths of light in nature. The wavelength range of light recognized by the human eye is between 320nm-760nm, and the light exceeding 320nm-760nm cannot be seen by the human eye; while the imaging components of the camera CCD or CMOS can see absolutely most wavelengths of light. Due to the participation of various lights, the color restored by the camera and the color seen by the naked eye have deviations in color. For example, green plants become grayish white, red pictures become light red, black becomes purple, etc. At night, due to the filtering effect of the double-peak filter, the CCD cannot make full use of all the light, and the phenomenon of no snowflake noise and its low-light performance are unsatisfactory. In order to solve this problem, IR-CUT double filter is used.
IR-CUT double filter refers to a set of filters built in the camera lens group. When the infrared sensor point outside the lens detects the change of light intensity, the built-in IR-CUT automatically switches the filter according to the external The intensity of the light is automatically switched accordingly, so that the image can achieve the best effect. That is to say, in day or night, the double filter can automatically switch the filter, so no matter in day or night, the best imaging effect can be obtained.
2.3.1 IR-CUT composition and principle
The IR CUT double filter switcher consists of an infrared cut-off low-pass filter (an infrared cut-off or absorption filter), a full-spectrum optical glass (a full-transmission spectral filter), a power mechanism (which can be electromagnetic , motor or other power source) and the shell, it is switched and positioned through a circuit control board. When the daytime light is sufficient, the circuit control board drives the switcher to switch and position to work with the infrared cut-off filter, and the CCD or CMOS restores the true color; when the visible light is insufficient at night, the infrared cut-off filter is automatically removed, full-spectrum optics The glass starts to work. At this time, it can sense the infrared light of the infrared lamp, so that the CCD or CMOS can make full use of all the light, thereby greatly improving the night vision performance of the infrared camera, and the whole picture is clear and natural.
2.3.2 IR-CUT index
a. The infrared cut-off degree, light transmittance, and light shaping effect of the filter.
b. Power drive part
c. Control circuit
4. Optical filter: IR Coating or blue glass is generally used to filter out infrared light.
2.4 Sensors
Image sensor (image sensor) is a semiconductor chip with millions to tens of millions of photodiodes on its surface. When the photodiodes are illuminated, they will generate charges and convert light into electrical signals. Its function is similar to human eyes, so the performance of the sensor will directly affect the performance of the camera.
2.4.1 Sensor structure
2.4.2 Classification
Photosensitive element: CCD, CMOS (PPS and APS)
Different processes: front-illuminated FSI, back-illuminated BSI, stacked
2.4.3 Indicators
1. Pixels
The sensor has many light-sensitive cells that convert light into electrical charges, which form an electronic image corresponding to the scene. In the sensor, each photosensitive unit corresponds to a pixel (Pixels). The more pixels, it means that it can sense more object details, so the image is clearer. The higher the pixel, the clearer the imaging effect. The product of camera resolution is the pixel value, for example: 1280×960=1228800
2. Target size
The size of the photosensitive part of the image sensor, generally expressed in inches. Like a TV, this data usually refers to the diagonal length of the image sensor, such as 1/3 inch, the larger the target surface, the better the light transmission, and the smaller the target surface, the easier it is to obtain Greater depth of field.
3. Sensitivity
It is to sense the intensity of incident light through CCD or CMOS and related electronic circuits. The higher the sensitivity, the stronger the sensitivity of the photosensitive surface to light, and the higher the shutter speed, which is especially important when shooting sports vehicles and night surveillance.
4. Electronic shutter
is a term coined in reference to the mechanical shutter function of a camera. It controls the light-sensing time of the image sensor. Since the light-sensing value of the image sensor is the accumulation of signal charges, the longer the light-sensing time, the longer the signal charge accumulation time, and the greater the amplitude of the output signal current. The faster the electronic shutter, the lower the sensitivity, which is suitable for shooting under strong light.
5. Frame rate
It refers to the number of pictures recorded or played per unit time. Continuously playing a series of pictures will produce an animation effect. According to the human visual system, when the playback speed of the picture is greater than 15 frames per second (that is, 15 frames), the human eye can hardly see the jump of the picture; when it reaches 24 frames /s——When 30 frames/s (that is, between 24 frames and 30 frames), the flicker phenomenon is basically not noticeable.
Frames per second (fps) or frame rate indicates how many times per second the graphics sensor is able to update while processing the field. A high frame rate results in a smoother, more realistic visual experience.
6. Signal-to-noise ratio
is the ratio of the signal voltage to the noise voltage, and the unit of the signal-to-noise ratio is expressed in dB. Generally, the signal-to-noise ratio value given by the camera is the value when the AGC (Automatic Gain Control) is turned off, because when the AGC is turned on, the small signal will be boosted, so that the noise level will also increase accordingly.
The typical value of the signal-to-noise ratio is 45-55dB. If it is 50dB, the image has a small amount of noise, but the image quality is good; if it is 60dB, the image quality is excellent and there is no noise. The better the control. The number of noise points in the image related to this parameter, the higher the signal-to-noise ratio, the cleaner the picture is, and the less point-like noise in the night vision picture.
2.5 DSPs
Digital Signal Processor DSP (DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING) function: mainly through a series of complex mathematical algorithm operations to optimize the digital image signal parameters, and transmit the processed signal to PC and other equipment through USB and other interfaces
2.5.1 Difference between DSP and ISP
Glossary:
ISP is the abbreviation of Image Signal Processor, which is the image signal processor.
DSP is the abbreviation of Digital Signal Processor, that is, digital signal processor.
Function explanation:
ISP is generally used to process the output data of Image Sensor (image sensor), such as AEC (automatic exposure control), AGC (automatic gain control), AWB (automatic white balance), color correction, Lens Shading, Gamma correction, and eliminate dead pixels , Auto Black Level, Auto White Level and other functions.
DSP has more functions, it can do some photos and echo (JPEG codec), video and playback (Video codec), H.264 codec, and many other processing, in short, processing digital signal.