Camera module and related concepts
October 7, 2023
1. Basic structure of Camera module
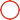
![]()
The core structure is Lens, IR Filter and Sensor.
Lens is composed of several lenses. Glass lenses have good imaging effects but high cost. The advantage of multiple lenses is that they can filter, converge, and correct light layer by layer.
IR Filter is an infrared filter;
Sensor is the core component, which functions like the film of a film camera and is responsible for imaging. There are two types: CCD and CMOS. CCD has better sensitivity and resolution and is generally used in digital cameras. CMOS has better cost, yield and power consumption and is generally used in mobile phones.
Lens main technical parameters
Resolution: Resolution of the camera, which is related to the resolution of the lens and sensor.
FoV (Field of View): Can shoot wide angles.
Focus Length: The distance from the focal point of the lens to the center of the lens. The image is clearest at the focal point. Depth of field DOF: The area in front and behind the focus that remains clear within a certain range. It is related to aperture, object distance, focal length and sensor. The larger the aperture or the closer you are to the object, the smaller the depth of field.
Aperture coefficient F: F (aperture coefficient value) = f (focal length) / D (aperture hole diameter). In actual use, the aperture coefficient is usually used to indirectly express the relative aperture size, such as f/1.4, f/2, f/2.8, etc., f/1.4 is equivalent to F1.4. The reciprocal of the aperture coefficient is called the relative aperture. Aperture controls the amount of light, depth of field, and image quality.
TV distortion: barrel or pincushion distortion.
Sensor main technical indicators
Sensitivity ISO: The sensor's sensitivity to light.
Dark shading/current (mv/sec, pA/cm2): sensor image noise. The voltage value generated by a pixel in 1 second at room temperature in a completely dark environment.
Dynamic Range (dB): The ratio of the maximum unsaturated photocurrent to the minimum detectable photocurrent. DR = 20log10(i_max / i_min).
Signal-to-Noise ratio (dB): The ratio of signal voltage to noise voltage.
White balance: Restore white objects to white under any light source. The accuracy indicator is the color difference ΔC between the actual color of the 18-degree gray card and the ideal color after the white balance is stabilized, which should generally be within 10.
2. Camera related concepts
AF (Auto Focus) automatic focus.
OIS (Optical Image Stabilizer) optical image stabilization device: anti-shake. Adjust the Compensation lens through negative feedback. Compared with traditional cameras, it has more gyroscopes, voice coil motors and driver ICs.
VCM (voice coil motor) voice coil motor: used for autofocus and anti-shake, and can adjust the lens position.