ISP and camera basics
July 7, 2023
Basic knowledge of camera
camera structure
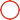
The commonly used structure is shown in the figure below, mainly including lens, base, sensor and PCB.
![]()
Types of camera modules
CCM is divided into 4 types: FF, MF, AF and ZOOM. FF (Fix Focus), fixed-focus camera, is currently the most used camera in China, and is used in 300,000 and 1.3 million mobile phone products. MF (Micro Focus), a two-speed zoom camera, is mainly used for close-up photos, such as mobile phones with business card recognition and barcode recognition, used for 1.3 million and 2 million mobile phone products. AF (Auto Focus), automatic zoom camera, mainly used in high-pixel mobile phones, also has the function of MF, used in 2 million and 3 million mobile phone products. Zoom (Auto Zoom), an automatic digital zoom camera, is mainly used in camera phones, similar to the quality of camera images, and is used in mobile phone products with more than 3 million.
How the camera works:
The optical image generated by the scene (SCE) through the lens (LENS) is projected onto the surface of the image sensor (Sensor), then converted into an electrical signal, converted into a digital image signal by A/D (analog-to-digital conversion), and then sent to the digital signal It is processed in the processing chip (DSP), and then transmitted to the CPU for processing through the I/O interface, and the image can be seen through DISPLAY.
![]()
Basic knowledge of Sensor
How Sensors work
The role of Lens is to filter out invisible light, let visible light enter, and project onto the Sensor. The working principle of Sensor: light --> charge --> weak current --> RGB digital signal waveform --> YUV digital signal signal
Sensor classification
Different types of components are divided into: CCD and CMOS. CCD (Charge Coupled Device,) is generally a high-end technical component used in photography and videography. The advantages of CCD are high sensitivity, low noise, and high signal-to-noise ratio. However, the production process is complicated, the cost is high, and the power consumption is high. CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) is used in products with lower image quality. The advantages of CMOS are high integration, low power consumption (less than 1/3 of CCD), and low cost. However, the noise is relatively large and the sensitivity is low. For CMOS, it is convenient for mass production, fast, and low in cost, which will be the development direction of the key components of digital cameras. CMOS photoreceptors have gradually replaced CCD photoreceptors, and are expected to become mainstream photoreceptors in the near future.
Sensor packaging form
There are two types of packaging for Sensor: CSP and DICE. In the processing and manufacturing of module manufacturers, the process corresponding to CSP is SMT, and the process corresponding to DICE is COB.
Basic block diagram of Sensor
The block diagram of the Sensor is shown in the figure (taking OV2718 as an example):
![]()
Basic knowledge of ISPs
Definition of ISP
ISP (Image Signal Processor), that is, image processing, the main function is to post-process the signal output by the front-end image sensor. The main functions include linear correction, noise removal, bad point removal, interpolation, white balance, automatic exposure control, etc. Thanks to ISP, it is possible to better restore scene details under different optical conditions.
How ISPs Work
The image from the Sensor side is a Bayer image, after black level compensation, lens correction, bad pixel correction, color interpolation, Bayer noise removal, white balance, color correction, Gamma correction, color space conversion (RGB to YUV), in In the YUV color space, color noise removal and edge enhancement, color and contrast enhancement, automatic exposure control, etc. are performed in the middle, and then the data in YUV (or RGB) format is output, and then transmitted to the CPU through the I/O interface for processing. (Take OV495 as an example)
![]()
ISP image processing algorithm
AE ( Automatic Exposure )
Automatic exposure refers to automatically adjust the exposure according to the intensity of the light, prevent overexposure or underexposure, and achieve appreciation brightness levels or so-called target brightness levels in different lighting conditions and scenes, so that the captured video or image is neither too dark nor too dark. Not too bright.
![]()
HDR ( High-Dynamic Range Imaging ) high dynamic range imaging
The dynamic range of the Sensor is the ability of the Sensor to reflect both highlights and shadows in an image. In the real situation in nature, the dynamic range of some scenes is greater than 100 dB, and the dynamic range of the human eye can reach 100 dB. The goal of HDR imaging is to correctly represent the real-world brightness range. Applicable scenes: It is more suitable for use in high-contrast scenes with backlight, such as: sunsets, indoor windows, so that the scenes in bright places will not be overexposed, and the scenes in dark places will not be underexposed.
![]()
AWB ( Auto White Balance ) automatic white balance
White balance is to find the white block in the image under different light conditions, and then adjust the ratio of R/G/B to offset the color cast, and restore the white object to a white object, making it closer to the visual habits of the human eye.
![]()
CCM ( Color Correction Matrix ) color correction
Color correction is mainly to correct the color error caused by the color penetration between the color blocks at the filter plate. The general process of color correction is to first compare the image captured by the image sensor with the standard image, and calculate a correction matrix based on this. This matrix is the color correction matrix of the image sensor. During the application of the image sensor, the matrix can be used to correct all images captured by the image sensor, so as to obtain an image closest to the real color of the object.
![]()
DNS ( Denoise ) denoising
Using a CMOS Sensor to acquire an image, lighting levels and sensor issues are the main factors that generate a lot of noise in the image. At the same time, when the signal passes through the ADC, some other noise will be introduced. These noises will blur the image as a whole and lose a lot of details, so it is necessary to denoise the image. Traditional methods of spatial denoising include mean filtering and Gaussian filtering.
![]()